|
@@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
|
|
|
|
|
+# [NLP]基于CNN对THUCNews数据集进行文本分类
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+简洁版数据集下载: [数据下载地址](https://www.heywhale.com/mw/dataset/5de4b6d0ca27f8002c4c530a)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+所用的数据集为清华NLP组提供的THUCNews新闻文本分类数据集的一个子集(原始的数据集大约74万篇文档,训练起来需要花较长的时间)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+本次训练使用了其中的体育, 财经, 房产, 家居, 教育, 科技, 时尚, 时政, 游戏, 娱乐10个分类,每个分类6500条,总共65000条新闻数据
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+数据集划分如下:
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+- cnews.train.txt: 训练集(50000条)
|
|
|
|
|
+- cnews.val.txt: 验证集(5000条)
|
|
|
|
|
+- cnews.test.txt: 测试集(10000条)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+## 数据预处理
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+导入需要的包
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+import os
|
|
|
|
|
+import pandas as pd
|
|
|
|
|
+import numpy as np
|
|
|
|
|
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
|
|
|
+import seaborn as sns
|
|
|
|
|
+from sklearn import metrics
|
|
|
|
|
+from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder,OneHotEncoder
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.models import Model
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.layers import LSTM, Activation, Dense, Dropout, Input, Embedding
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.layers import Convolution1D,BatchNormalization,concatenate,Flatten
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.preprocessing import sequence
|
|
|
|
|
+from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
|
|
|
|
|
+%matplotlib inline
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+import sys
|
|
|
|
|
+from collections import Counter
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+import numpy as np
|
|
|
|
|
+import tensorflow.keras as kr
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+初始化文件路径
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+train_dir = 'cnews.train.txt'
|
|
|
|
|
+test_dir = 'cnews.test.txt'
|
|
|
|
|
+val_dir = 'cnews.val.txt'
|
|
|
|
|
+vocab_dir = 'cnews.vocab.txt'
|
|
|
|
|
+save_dir = 'checkpoints/textcnn'
|
|
|
|
|
+save_path = 'best_validation'
|
|
|
|
|
+if not os.path.exists(vocab_dir): # 如果不存在词汇表,重建
|
|
|
|
|
+ build_vocab(train_dir, vocab_dir, config.vocab_size)
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+创建数据类别映射、文本id映射字典
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+# 创建数据类别映射、文本字典
|
|
|
|
|
+categories, cat_to_id = read_category()
|
|
|
|
|
+words, word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
|
|
|
|
|
+vocab_size = len(words)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+def read_category():
|
|
|
|
|
+ """读取分类目录,固定"""
|
|
|
|
|
+ categories = ['体育', '财经', '房产', '家居', '教育', '科技', '时尚', '时政', '游戏', '娱乐']
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ categories = [native_content(x) for x in categories]
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ cat_to_id = dict(zip(categories, range(len(categories))))
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ return categories, cat_to_id
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+def read_vocab(vocab_dir):
|
|
|
|
|
+ """读取词汇表"""
|
|
|
|
|
+ with open_file(vocab_dir) as fp:
|
|
|
|
|
+ # 如果是py2 则每个值都转化为unicode
|
|
|
|
|
+ words = [native_content(_.strip()) for _ in fp.readlines()]
|
|
|
|
|
+ word_to_id = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
|
|
|
|
|
+ return words, word_to_id
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+处理原始数据
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+seq_length = 600 # 序列长度
|
|
|
|
|
+x_train, y_train = process_file(train_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id, seq_length)
|
|
|
|
|
+x_val, y_val = process_file(val_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id, seq_length)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+def process_file(filename, word_to_id, cat_to_id, max_length=600):
|
|
|
|
|
+ """将文件转换为id表示"""
|
|
|
|
|
+ contents, labels = read_file(filename)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ data_id, label_id = [], []
|
|
|
|
|
+ for i in range(len(contents)):
|
|
|
|
|
+ data_id.append([word_to_id[x] for x in contents[i] if x in word_to_id])
|
|
|
|
|
+ label_id.append(cat_to_id[labels[i]])
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ # 使用keras提供的pad_sequences来将文本pad为固定长度
|
|
|
|
|
+ x_pad = kr.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(data_id, max_length)
|
|
|
|
|
+ y_pad = kr.utils.to_categorical(label_id, num_classes=len(cat_to_id)) # 将标签转换为one-hot表示
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ return x_pad, y_pad
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+def read_file(filename):
|
|
|
|
|
+ """读取文件数据"""
|
|
|
|
|
+ contents, labels = [], []
|
|
|
|
|
+ with open_file(filename) as f:
|
|
|
|
|
+ for line in f:
|
|
|
|
|
+ try:
|
|
|
|
|
+ label, content = line.strip().split('\t')
|
|
|
|
|
+ if content:
|
|
|
|
|
+ contents.append(list(native_content(content)))
|
|
|
|
|
+ labels.append(native_content(label))
|
|
|
|
|
+ except:
|
|
|
|
|
+ pass
|
|
|
|
|
+ return contents, labels
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+## 模型构建
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+构建模型如下
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+#TextInception
|
|
|
|
|
+main_input = Input(shape=(600,), dtype='float64')
|
|
|
|
|
+embedder = Embedding(vocab_size + 1, 256, input_length = 600)
|
|
|
|
|
+embed = embedder(main_input)
|
|
|
|
|
+block1 = Convolution1D(128, 1, padding='same')(embed)
|
|
|
|
|
+conv2_1 = Convolution1D(256, 1, padding='same')(embed)
|
|
|
|
|
+bn2_1 = BatchNormalization()(conv2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+relu2_1 = Activation('relu')(bn2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+block2 = Convolution1D(128, 3, padding='same')(relu2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+inception = concatenate([block1, block2], axis=-1)
|
|
|
|
|
+flat = Flatten()(inception)
|
|
|
|
|
+fc = Dense(128)(flat)
|
|
|
|
|
+drop = Dropout(0.5)(fc)
|
|
|
|
|
+bn = BatchNormalization()(drop)
|
|
|
|
|
+relu = Activation('relu')(bn)
|
|
|
|
|
+main_output = Dense(10, activation='softmax')(relu)
|
|
|
|
|
+model = Model(inputs = main_input, outputs = main_output)
|
|
|
|
|
+model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
|
|
|
|
|
+ optimizer='adam',
|
|
|
|
|
+ metrics=['accuracy'])
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+开始训练
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
|
|
|
|
|
+ batch_size=32,
|
|
|
|
|
+ epochs=3,
|
|
|
|
|
+ validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+## 查看结果
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
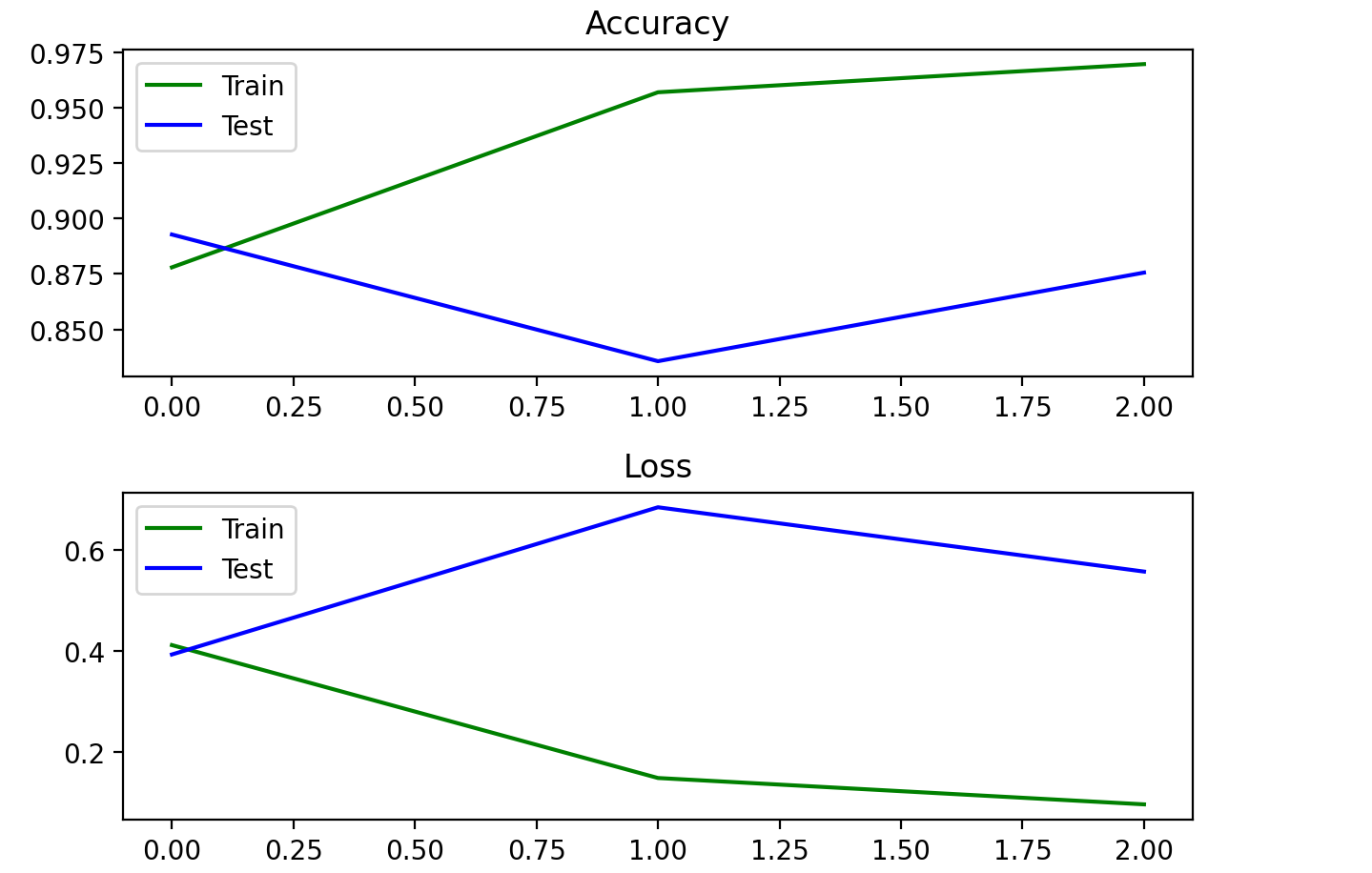
+画出loss与acc图像
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+# plot accuracy and loss
|
|
|
|
|
+def plot_acc_loss(history):
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.subplot(211)
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.title("Accuracy")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.plot(history.history["accuracy"], color="g", label="Train")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.plot(history.history["val_accuracy"], color="b", label="Test")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.legend(loc="best")
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.subplot(212)
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.title("Loss")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.plot(history.history["loss"], color="g", label="Train")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"], color="b", label="Test")
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.legend(loc="best")
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.tight_layout()
|
|
|
|
|
+ plt.show()
|
|
|
|
|
+plot_acc_loss(history)
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+## 使用模型进行预测
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 对测试集进行预测
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+## 对测试集进行预测
|
|
|
|
|
+y_pre = model1.predict(x_val)
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 对单个语句进行预测
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+test="我国用于载人登月的新一代载人火箭将于2030年前完成研制。“2030年前”这个时间让人心潮澎湃,更心怀期待。为能将中国人的脚印留在月球,无数航天人一步一个脚印,扎扎实实地推进着技术攻关。“仰望星空,脚踏实地”,这八个字特别适合中国航天。我们的目标是"
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+data_id=[]
|
|
|
|
|
+data_id.append([word_to_id[x] for x in test if x in word_to_id])
|
|
|
|
|
+# 使用keras提供的pad_sequences来将文本pad为固定长度
|
|
|
|
|
+x_pad = kr.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(data_id, 600)
|
|
|
|
|
+y_pre = model1.predict(x_pad)
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+y_pres=y_pre.tolist()
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+keys=list(cat_to_id.keys())
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+for pre in y_pres:
|
|
|
|
|
+ result={}
|
|
|
|
|
+ for i in range(10):
|
|
|
|
|
+ result[keys[i]]=pre[i]
|
|
|
|
|
+ result = sorted(result.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
|
|
|
|
|
+ print(result)
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+## 代码讲解
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 预处理
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+预处理部分主要为将txt文件中的文本信息读出
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+1. 获取词库(这里以单个文字为粒度,一般情况下会进行分词,这里由于数据集较小,防止由于分词后词库太小导致预测数据时大部分词找不到对应的词向量,所以采用单个文字的粒度)
|
|
|
|
|
+2. 建立每个词对应id的映射字典
|
|
|
|
|
+3. 将所有文本数据进行分词(这里以单个文字为粒度)
|
|
|
|
|
+4. 打散数据,分为测试集和训练集等
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 模型构建
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
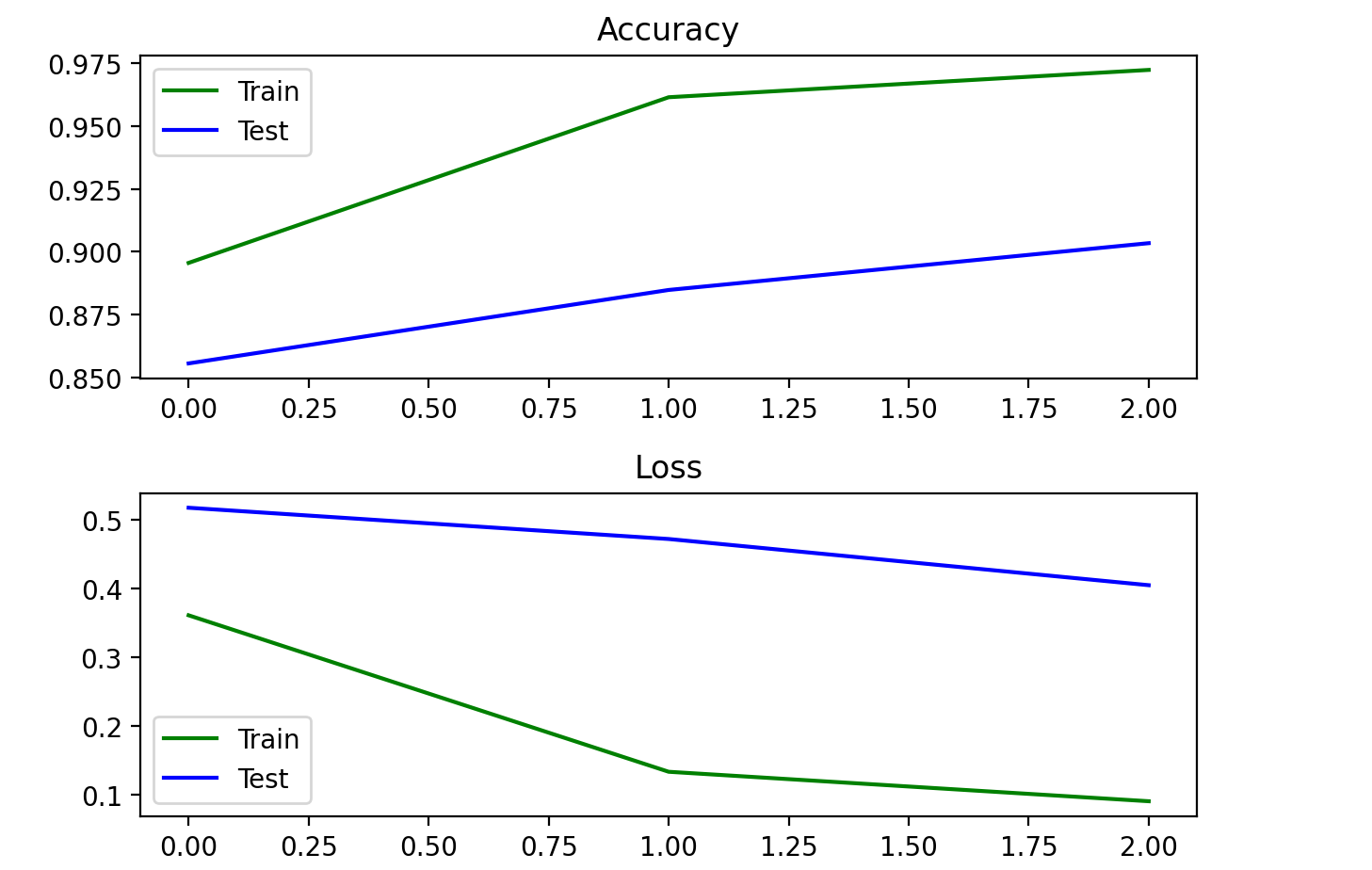
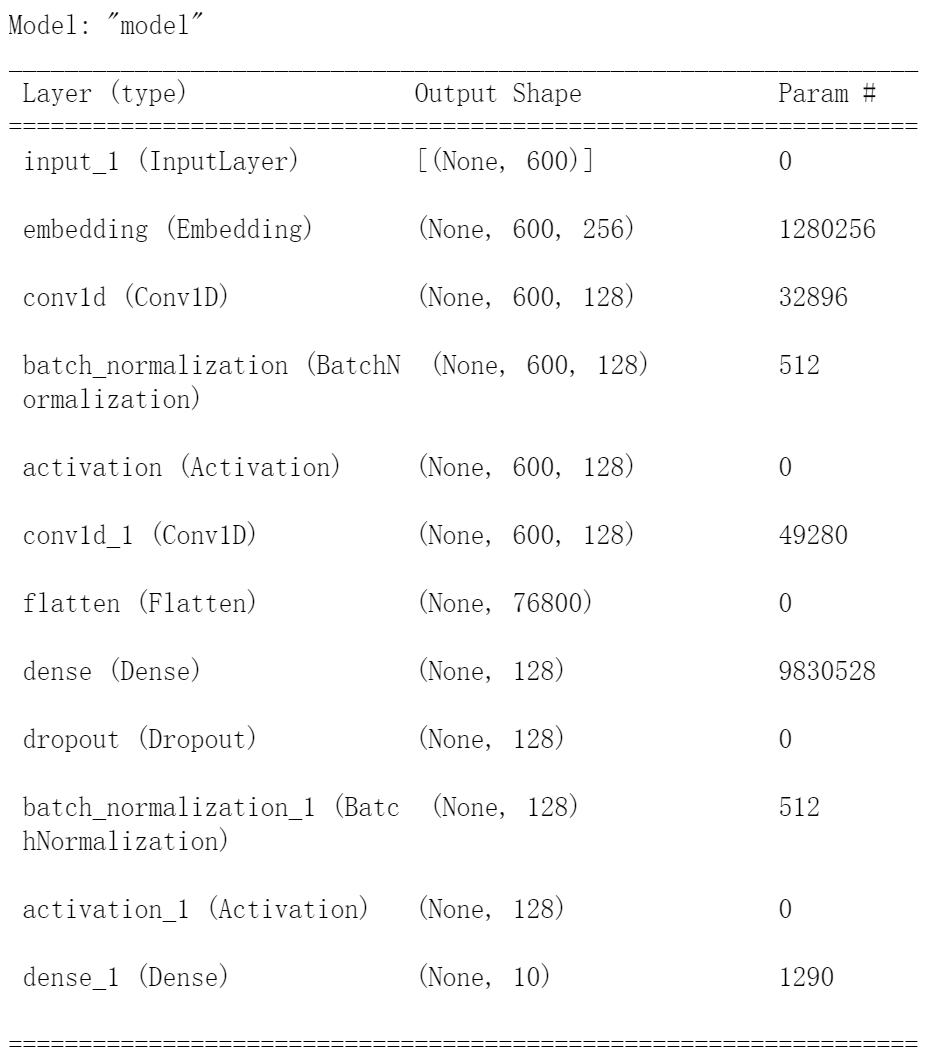
+这里改动了一下模型结构,效果更好
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+```python
|
|
|
|
|
+main_input = Input(shape=(600,), dtype='float64')
|
|
|
|
|
+embedder = Embedding(vocab_size + 1, 256, input_length = 600)
|
|
|
|
|
+embed = embedder(main_input)
|
|
|
|
|
+conv2_1 = Convolution1D(128, 1, padding='same')(embed)
|
|
|
|
|
+bn2_1 = BatchNormalization()(conv2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+relu2_1 = Activation('relu')(bn2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+conv2_2 = Convolution1D(128, 3, padding='same')(relu2_1)
|
|
|
|
|
+flat = Flatten()(conv2_2)
|
|
|
|
|
+fc = Dense(128)(flat)
|
|
|
|
|
+drop = Dropout(0.5)(fc)
|
|
|
|
|
+bn = BatchNormalization()(drop)
|
|
|
|
|
+relu = Activation('relu')(bn)
|
|
|
|
|
+main_output = Dense(10, activation='softmax')(relu)
|
|
|
|
|
+model = Model(inputs = main_input, outputs = main_output)
|
|
|
|
|
+model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
|
|
|
|
|
+ optimizer='adam',
|
|
|
|
|
+ metrics=['accuracy'])
|
|
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+- 输入层:这里限制了单条文本的max_length为600
|
|
|
|
|
+- embedding层:这是嵌入层,目的是将输入序列中的整数索引转换成一个稠密的向量(词向量),嵌入层的输入是一个2D张量,形状为`(batch_size, sequence_length)`,输出是3D张量,形状为`(batch_size, sequence_length, output_dim)`(如果不使用预训练词向量模型,嵌入层是用随机权重进行初始化,在训练中将学习到训练集中的所有词的权重,也就是词向量)
|
|
|
|
|
+- conv1d层:卷积层
|
|
|
|
|
+- BatchNormalization层:通过规范化的手段,将越来越偏的分布拉回到标准化的分布,使得激活函数的输入值落在激活函数对输入比较敏感的区域,从而使梯度变大,加快学习收敛速度,避免梯度消失的问题
|
|
|
|
|
+- 激活层:激活函数
|
|
|
|
|
+- flatten层:降维扁平化
|
|
|
|
|
+- dense层:全连接层
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 预测以及模型的保存、读取
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+都是一些keras内置的API,不再赘述
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+### 预训练词向量
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+这里对预训练词向量多提一嘴
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+词向量是指用一组数值来表示一个汉字或者词语,这也是因为计算机只能进行数值计算。最简单的方法是one-hot,假如总的有一万个词,那词向量就一万维,词对应的那维为1,其他为0,但这样的表示维度太高也太稀疏了,所以后来就开始研究用一个维度小的稠密向量来表示,现在的词向量一般都128,200或者300维,就很小了
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+预训练指提前训练好这种词向量,对应的是一些任务可以输入词id,然后在做具体的任务内部训练词向量,这样出来的词向量不具有通用性,而预训练的词向量,是在极大样本上训练的结果,有很好的通用性,无论什么任务都可以直接拿来用
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
+在本例中没有使用预训练的词向量,直接用嵌入层随机生成再迭代训练了,一般情况下会使用一些预训练好的词向量模型的
|