commit
f919f838c2
100 fichiers modifiés avec 7817 ajouts et 0 suppressions
+ 10
- 0
.dockerignore
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 11
- 0
.gitignore
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 16
- 0
.readthedocs.yaml
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 201
- 0
LICENSE
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 14
- 0
Makefile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 95
- 0
README.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 17
- 0
docker/base.Dockerfile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 9
- 0
docker/client.Dockerfile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 105
- 0
docker/docker-compose.yml
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 9
- 0
docker/run.Dockerfile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 9
- 0
docker/server.Dockerfile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 9
- 0
docker/tracker.Dockerfile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 20
- 0
docs/en/Makefile
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 6
- 0
docs/en/_static/css/readthedocs.css
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
BIN
docs/en/_static/image/architecture.png
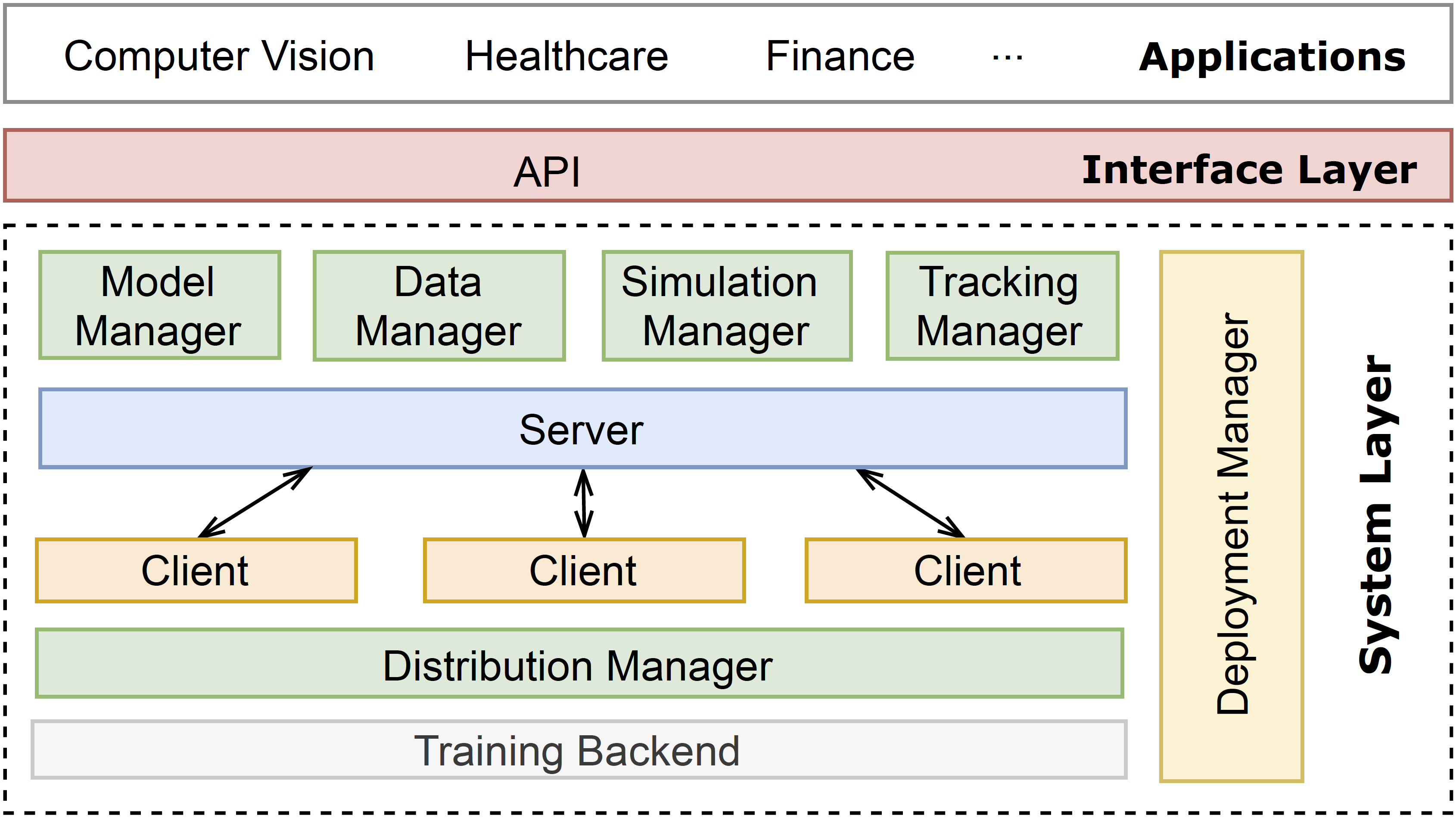
BIN
docs/en/_static/image/docker.png
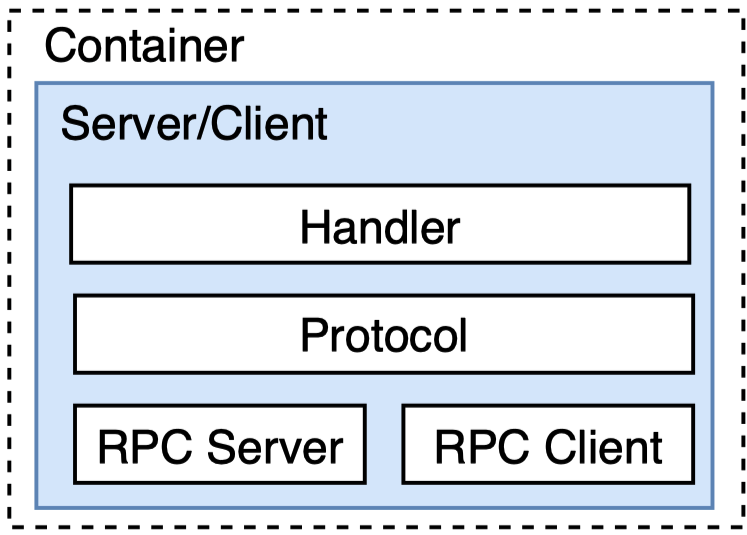
BIN
docs/en/_static/image/easyfl-logo.png

BIN
docs/en/_static/image/registry.png
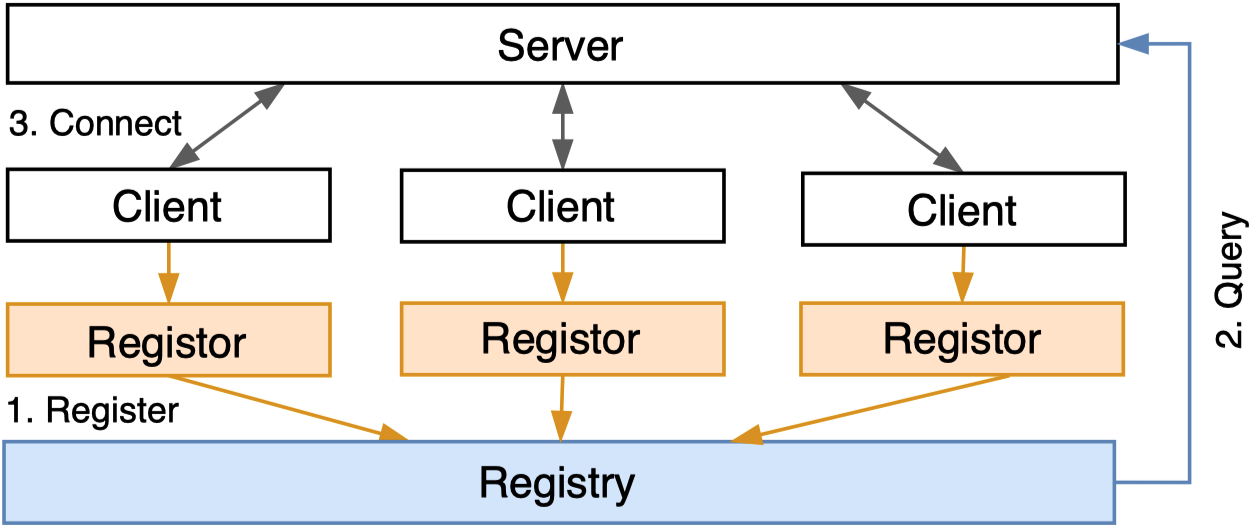
BIN
docs/en/_static/image/training-flow.png
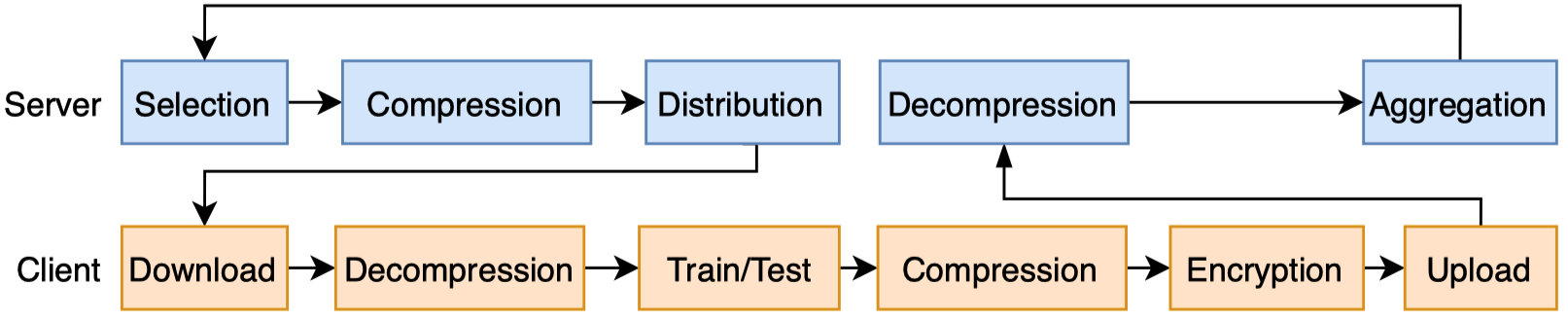
+ 40
- 0
docs/en/api.rst
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 5
- 0
docs/en/changelog.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 125
- 0
docs/en/conf.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 8
- 0
docs/en/faq.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 87
- 0
docs/en/get_started.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 48
- 0
docs/en/index.rst
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 51
- 0
docs/en/introduction.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 35
- 0
docs/en/make.bat
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 11
- 0
docs/en/projects.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 49
- 0
docs/en/quick_run.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 318
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/config.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 281
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/customize_server_and_client.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 232
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/dataset.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 42
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/distributed_training.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 126
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/high-level_apis.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 11
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/index.rst
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 92
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/model.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 257
- 0
docs/en/tutorials/remote_training.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 22
- 0
easyfl/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 5
- 0
easyfl/client/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 471
- 0
easyfl/client/base.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 30
- 0
easyfl/client/service.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 3
- 0
easyfl/communication/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 77
- 0
easyfl/communication/grpc_wrapper.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/compression/__init__.py
+ 113
- 0
easyfl/config.yaml
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 481
- 0
easyfl/coordinator.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 26
- 0
easyfl/datasets/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 0
easyfl/datasets/cifar10/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
+ 88
- 0
easyfl/datasets/cifar10/cifar10.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 0
easyfl/datasets/cifar100/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
+ 88
- 0
easyfl/datasets/cifar100/cifar100.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 243
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/__init__.py
+ 55
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/cifar10.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 55
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/cifar100.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 10
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/femnist.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 142
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/language_utils.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 15
- 0
easyfl/datasets/data_process/shakespeare.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 427
- 0
easyfl/datasets/dataset.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 45
- 0
easyfl/datasets/dataset_util.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
+ 109
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/femnist.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/__init__.py
+ 94
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/data_to_json.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 71
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/get_file_dirs.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 55
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/get_hashes.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 25
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/group_by_writer.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 25
- 0
easyfl/datasets/femnist/preprocess/match_hashes.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
+ 89
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/shakespeare.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/utils/__init__.py
+ 17
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/utils/gen_all_data.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 183
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/utils/preprocess_shakespeare.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 69
- 0
easyfl/datasets/shakespeare/utils/shake_utils.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 350
- 0
easyfl/datasets/simulation.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/__init__.py
+ 158
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/base_dataset.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 2
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/constants.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 176
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/download.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 62
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/remove_users.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 274
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/sample.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 235
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/split_data.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 42
- 0
easyfl/datasets/utils/util.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 18
- 0
easyfl/distributed/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 257
- 0
easyfl/distributed/distributed.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 64
- 0
easyfl/distributed/slurm.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/encryption/__init__.py
+ 1
- 0
easyfl/models/__init__.py
|
||
|
||
+ 36
- 0
easyfl/models/lenet.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 24
- 0
easyfl/models/model.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 124
- 0
easyfl/models/resnet.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 102
- 0
easyfl/models/resnet18.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 107
- 0
easyfl/models/resnet50.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 36
- 0
easyfl/models/rnn.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 40
- 0
easyfl/models/simple_cnn.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 65
- 0
easyfl/models/vgg9.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 0
- 0
easyfl/pb/__init__.py
+ 75
- 0
easyfl/pb/client_service_pb2.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 66
- 0
easyfl/pb/client_service_pb2_grpc.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||