intersect.md 9.9 KB
Intersection
This module provide some method of PSI(Private Set Intersection)
RSA Intersection
This mode implements algorithm based on RSA Intersection. This work is built on FATE, eggroll and federation API that construct the secure, distributed and parallel infrastructure.
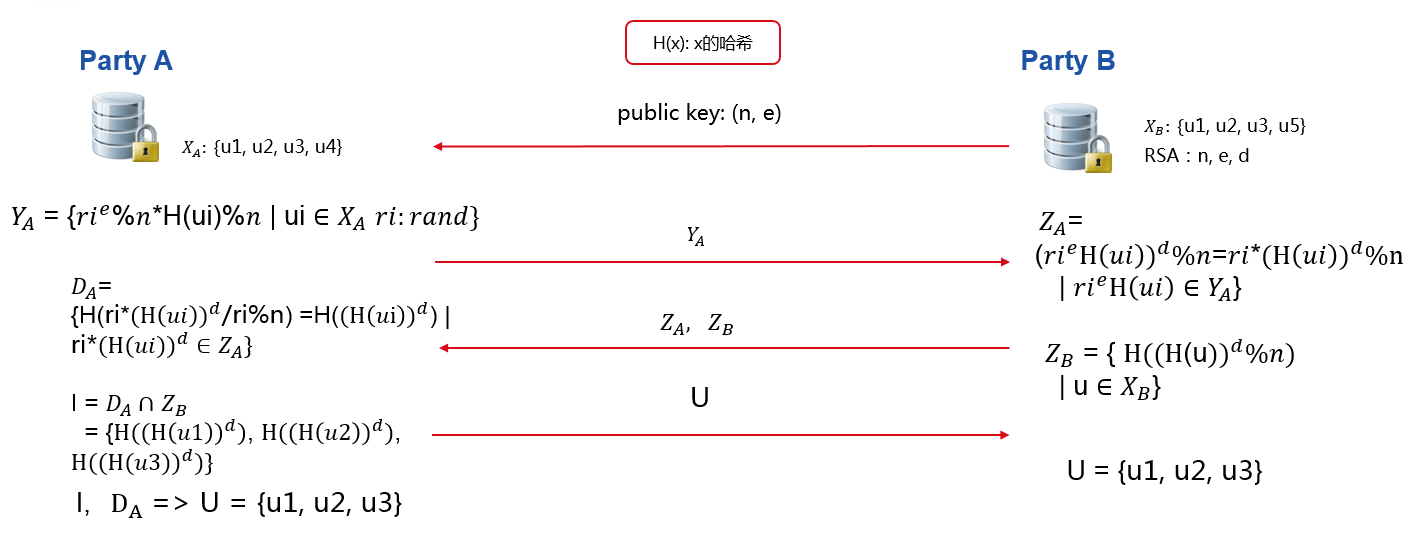
Our Intersection module tries to solve Privacy-Preserving Entity Match problem. This module helps two and more parties to find common entry ids without leaking non-overlapping ids. The process is illustrated below in figure 1.
In figure 1 ,Party A has user id u1,u2,u3,u4, while Party B has u1,u2,u3,u5. After Intersection, party A and party B both learn their common user ids, which are u1,u2,u3, while neither party A nor B could decrypt each other's non-overlapping user ids. Transmission parties' processed id to the other party, like (Y-A) and (Z-B), will not reveal raw ids. Processed (Z-B) is safe due to the privacy key of party B. Each (Y-A) includes different random value which binds to each value in (X-A) and will be safe as well.
Introduced in FATE version 1.6, split_calculation option is available for improved efficiency. Different from unified process described above, split_calculation process first splits hash-processed ids into even and odd groups; each group then runs through the RSA intersection process with either host or guest as the joining role. Note than with split_calculation, host(s) always know about their common even ids with guest since they are responsible for finding common even ids.
With RSA intersection, participants can get their intersection ids securely and efficiently.
RAW Intersection
This mode implements the simple intersection method in which a participant sends all its ids to another participant, and the other participant finds their common ids. Finally, the joining role will send the intersection ids to the sender.
DH Intersection
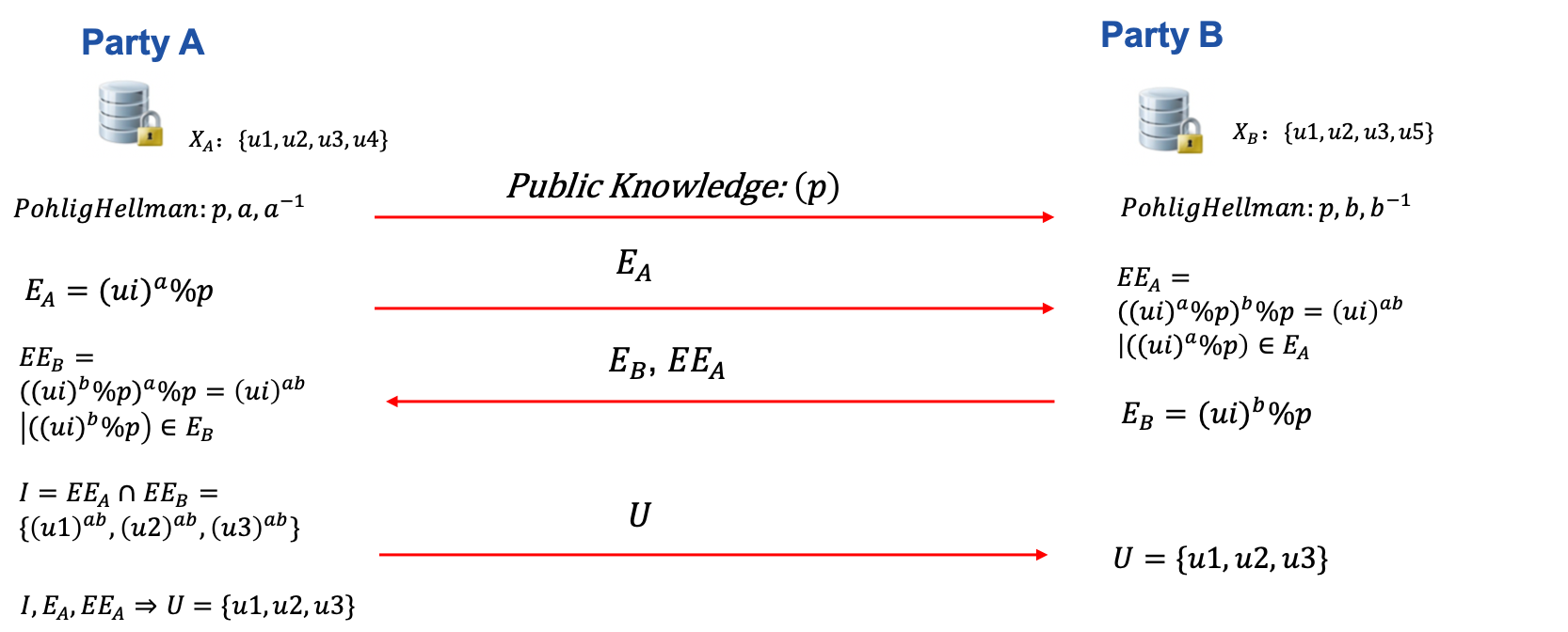
This mode implements secure intersection based on symmetric encryption with Pohlig–Hellman commutative cipher. DH Intersection is also used in Secure Information Retrieval(SIR) module.
Below is an illustration of single-host-guest DH intersection.
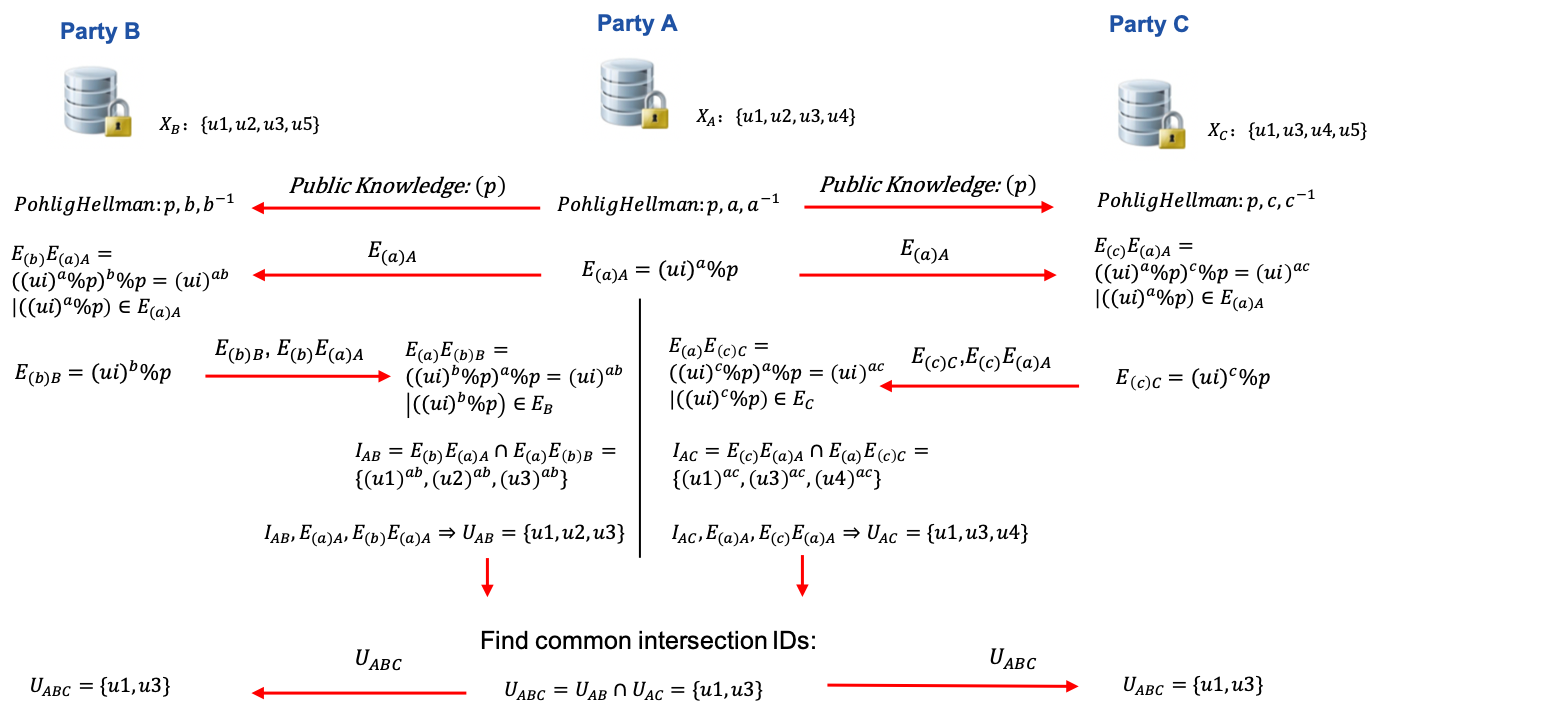
Here is an illustration of DH intersection with multiple hosts.
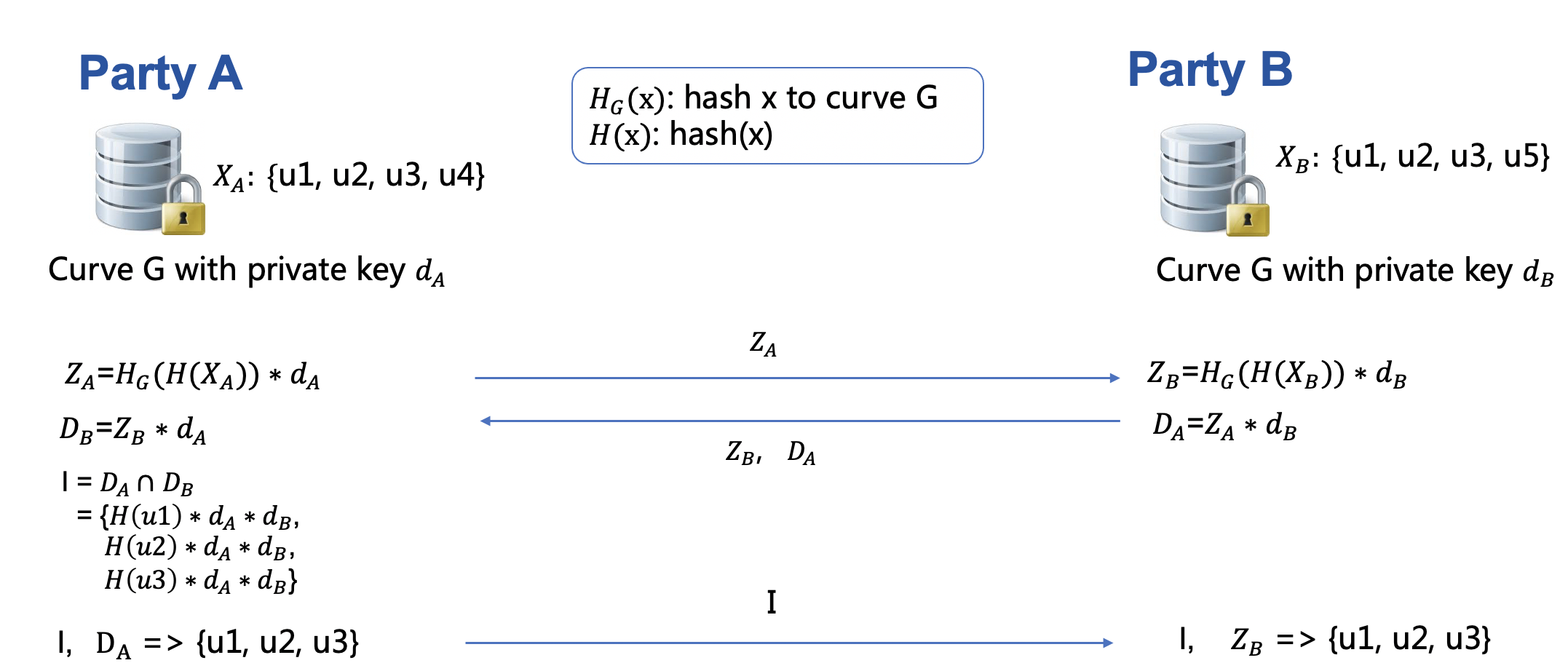
ECDH Intersection
This mode implements secure intersection
based on elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman scheme.
ECDH mode currently uses Curve25519,
which offers 128 bits of security with key size of 256 bits.
Below is an illustration of ECDH intersection. Note that currently ECDH method only supports single-host scenario.
For details on how to hash value to given curve, please refer here.
Intersection With Cache
Intersection may be conducted as online/offline phases. Both RSA and DH Intersection support cache.
Multi-Host Intersection
RSA, RAW, and DH intersection support multi-host scenario. It means a guest can perform intersection with more than one host simultaneously and get the common ids among all participants.
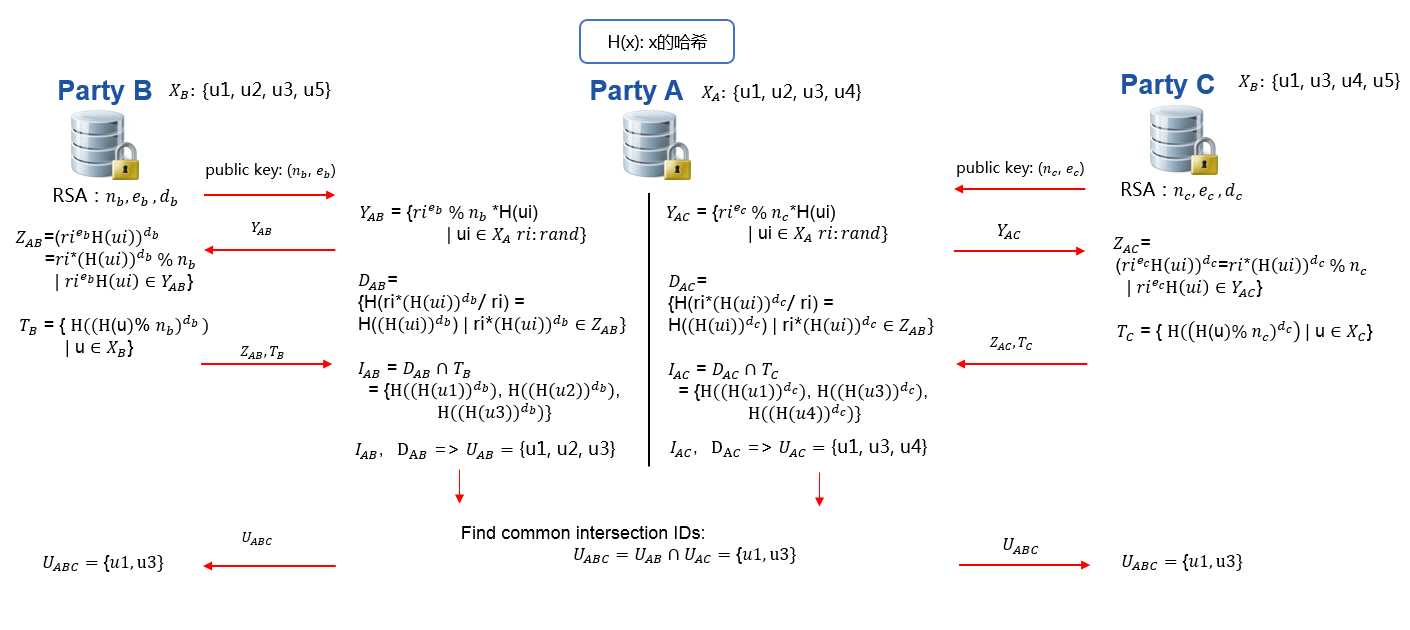
Refer to figure 2 for a demonstration of one guest running intersection with two hosts; the same process applies to cases with more than two hosts. First, guest will run intersection with each host and get respective overlapping ids. Then, guest will find common IDs from all intersection results. Optionally, guest will send common IDs to every host.
Match ID(Repeated ID) intersection
Starting at ver 1.7, it is recommended to assign random sid to uploaded data. Intersection module then automatically checks for and process data with instance ID.
Note that parameters for original repeated ID process such as
repeated_id_process are deprecated in
ver 1.7. Specify sample_id_generator to the
role whose sid to be kept. For instances, when
sample_id_generator is set to Guest(default),
Guest's data is
sid, id, value
123, alice, 2
125, alice, 3
130, bob, 4
In Host, you data is
sid, id, value
210, alice, 5
232, alice, 5
212, bob, 4
After intersection, guest will get the intersection results:
sid, id, value
123, alice, 2
125, alice, 3
130, bob, 4
And for Host:
sid, id, value
123, alice, 5
125, alice, 5
130, bob, 4
Feature
Below lists features of each ECDH, RSA, DH, and RAW intersection methods.
| Intersect Methods | PSI | Match-ID Support | Multi-Host | Exact-Cardinality | Estimated Cardinality | Preprocessing | Cache |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECDH | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RSA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| DH | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RAW | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
All four methods support:
- Automatically match ID intersection using ID expanding (when data contains instance id).
- Configurable hashing methods, including sha256, md5, and sm3; hash operators of RSA intersection can be configured separately, please refer here for more details.
- Preprocessing step to pre-filter Host's data for faster PSI
- Multi-host PSI task. The detailed configuration for multi-host task can be found here.
RSA, DH, ECDH intersection methods also support:
- PSI with cache
RAW intersection supports the following extra feature:
- base64 encoding may be used for all hashing methods.
Cardinality Computation:
Set
cardinality_methodtorsawill produce estimated intersection cardinality;Set
cardinality_methodtodhorecdhwill compute exact intersection cardinality