positive_unlabeled.md 2.9 KB
Positive Unlabeled Learning
Introduction
Positive unlabeled learning is one of the semi-supervised algorithms. The corresponding component is applied to hetero-classification tasks of Federated Learning, in particular, learning classifiers from both positive and unlabeled data.
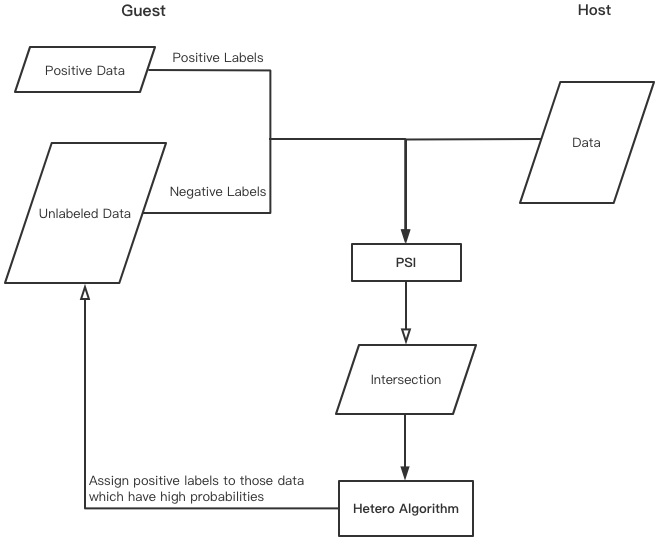
In the component, unlabeled data are treated as negative data for the binary classifier training. The trained classification model is used for assigning labels to those unlabeled data. After labeling operations, the dataset is repartitioned and the number of labeled data is increased. Repeatedly, we can gain a model that takes advantage of unlabeled data. The procedure of probability labeling strategy is shown below.
Usage
Positive unlabeled learning has the following precautions.
- The unlabeled digit should be set to 0. If not, use Label Transform component to convert the value.
- Freely connect the combination of hetero binary classifier and Positive Unlabeled components in DSL or pipeline. For instance, we can build a DAG with such two combinations.
The examples of positive unlabeled learning can be referred to DSL and Pipeline.
Features
Positive unlabeled learning provides different labeling strategies.
- Probability strategy uses a preset probability p as the threshold. If the predicted probability of unlabeled samples is not less than p, we can treat these data as positive ones.
- Quantity strategy sets a preset quantity q as the threshold. Given the unlabeled samples sorted from high to low predicted probability, we select the first q data as positive ones.
- Proportion strategy takes a preset proportion r as the threshold. Given all the samples sorted from high to low predicted probability, we pick the first r percent data as positive ones.
- Distribution strategy computes a ratio between the unlabeled count and total number, and adopts a preset scale s as the threshold. Intuitively, the number of converted data should decrease as the number of iterations increases. Such a ratio satisfies the discipline of gradually reducing. Given all the samples sorted from high to low predicted probability, we choose the first s * ratio data as positive ones.
The parameters of positive unlabeled learning are listed below.
strategy: The strategy of converting unlabeled value, including"probability","quantity","proportion"and"distribution"threshold: The threshold in labeling strategy, diverse semantics for different strategies
Application
Positive unlabeled learning currently supports the following situations.
- The dataset partition should be positive and unlabeled.
- The model of binary classification can be Hetero-LR, Hetero-SSHELR or Hetero-SecureBoost.